Get an Expert’s Guide to Currency Markets and How They Work
Currency markets are huge — the biggest in the world, in fact — and can be very confusing for beginners. There’s so much going on, how can an outsider ever hope to understand anything about it? But there’s good news. In this guide you’ll gain an understanding of exactly how currency markets work, and how it’s possible to make money from them.
How do currency markets work?
The global currency markets are where investors trade different foreign currencies against each other. The base currency is the first currency listed in a pair and is always equal to one unit. The counter, or quote currency, is the second currency listed in a pair and its value fluctuates relative to the base currency. Currencies are priced as pairs, with the price of one unit of the base currency quoted against units of the foreign exchange rate quoted for all other currencies. For example, if you want to buy Japanese yen (the base currency) with U.S. dollars (the quote or counter currency), you would look for a USD/JPY pairing on your broker’s platform and execute a buy order at that price level.
Currency prices can be affected by numerous factors like interest rates, inflation, political stability, economic growth prospects, and global events like natural disasters or terrorist attacks. The Currency Markets are open 24 hours per day from Sunday evening through Friday night EST because it encompasses trading activity from around the world. There are two main types of participants in forex markets: retail traders who trade for their own account using retail brokers; and large institutions that deal directly with each other via interbank liquidity providers. Because retail traders account for only a tiny fraction of total volume executed in FX markets, their actions have less impact on prices than those of institutional investors.
The most common way to trade the currency markets is through exchange-traded foreign exchange futures contracts. These contracts allow investors to bet on whether they believe that the price of one particular currency will rise or fall relative to another over some predetermined time period. Forex trading has become increasingly popular over recent years as online platforms make it easier than ever before for individual traders to get involved.
What are the benefits of currency trading?
There are many benefits to currency trading, including:
- 24 hour access: when market conditions are favorable, you can trade currencies 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
- Foreign currencies: You can trade in foreign currencies, which gives you exposure to new markets and investment opportunities.
- Exchange-traded Foreign Exchange Futures: Investors trade currencies on regulated exchanges just like they do stocks and other commodities. This provides transparency and liquidity to the marketplaces.
- Forex market hours: Global forex trading occurs 24 hours a day, from Sunday evening to Friday afternoon EST. This allows traders from all around the world to participate in this exciting marketplace whenever it is convenient for them. 5
- Base currency: When you trade currencies, your base currency is always denominated in US dollars (or another major currency). Your profits or losses will be quoted in terms of this base currency.
- Currency prices: Because the forex markets are so liquid (over $5 trillion is traded every day), spreads between buy and sell prices are typically very narrow. This means that traders can get into and out of positions quickly and at relatively low costs. 7
- Major Pairs: There are dozens of different pairs of foreign currencies that can be traded together. USD/JPY (US dollar vs Japanese yen), EUR/USD (euro vs US dollar), GBP/USD (British pound vs US dollar), AUD/USD (Australian dollar vs US dollar), USD/CAD (US dollar vs Canadian dollar), NZD/USD (New Zealand Dollar vs US Dollar), and others are among the most popular.
- Minor pairs: as well as being able to trade major pairs, traders also have access to dozens of minor pairs consisting of two less commonly traded currencies. These offer more opportunity for profit, but also carry greater risk due to their lower liquidity.
- Beginning traders: FX markets offer an excellent opportunity for beginning traders who want to learn about how currency markets work without risking large sums of money.
- Market conditions: While no market is risk-free, overall, foreign exchange markets are less volatile than stocks and provide opportunities that are not available elsewhere during both bull and bear markets.
What are the risks of Trading The currency markets?
Foreign exchange, also known as currency markets, or forex, is a global market where investors trade currencies. The forex currency markets are open 24 hours a day, five days a week. This makes it possible for investors to trade currencies around the clock. However, there are risks associated with trading currencies. Let’s take a look at some of these risks:
- Currencies’ prices can be very volatile and can move quickly up or down. This can lead to huge losses if you’re not careful. It’s important to stay informed about current market conditions and always use stop losses to protect your investment capital.
- The forex markets are highly leveraged and this can lead to large losses if you’re not careful. For example, if you invest $100 in a currency pair and the price moves against you by just 1%, you will lose $100!
- The foreign currency markets are extremely volatile and can be affected by many factors, including political events, economic news releases, etc. So it’s important to carefully research any potential trades before entering into them.
- There is no central exchange for the foreign exchange market, so prices may vary from broker-to-broker.
- Trading in the currency markets is complex and it takes time to learn how it works.
- Many beginning traders get suckered into buying high and selling low-which leads to big losses.
- Market conditions (elevated volatility levels; choppy price action; etc.) can cause havoc on even experienced traders’ accounts.
What is the best time to trade currencies?
There is no definitive answer to this question, as it depends on a variety of factors, including market conditions, the currencies involved, and your own personal trading style. However, there are some general guidelines that can help you make informed decisions when trading foreign currencies.
The global forex markets are open 24 hours a day from Sunday evening through Friday evening EST. During this time period, investors can trade currencies around the world in response to news events and changing market conditions. The most active times for currency trading are between 8 a.m. and 12 p.m. EST, when most of the major global markets overlap. This provides opportunities for greater liquidity and tighter spreads, two important factors when executing trades.
However, depending on your goals and risk tolerance, you may want to focus on different times of the day or week. For example, if you’re looking to take advantage of short-term price movements (day trading), then you’ll want to focus your activity during periods when volatility is highest, typically around economic releases or major news events. Conversely, if you’re looking for longer-term opportunities (swing trading), then focusing on quieter periods may be more advantageous since prices tend not to move as much over longer time frames.
What are the most popular currency pairs?
There are a number of different currency pairs that investors can trade on the forex market. The most popular currency pairs are those that involve the US dollar, such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD. These pairs are known as “major” currency pairs.
Other popular currency pairs include CAD/JPY, AUD/JPY, and NZD/JPY, which are known as “minor” or “exchange rate” currencies. These currencies tend to be more volatile than the majors, making them ideal for day traders who look to take advantage of short-term price movements.
The foreign exchange (FX) currency markets are open 24 hours a day from Sunday evening through Friday night EST. This makes it possible for investors around the world to trade these currencies at any time during the weekdays. However, liquidity is highest during London trading hours (8am–5pm GMT), when most of the world’s major banks and financial institutions participate in FX trading.
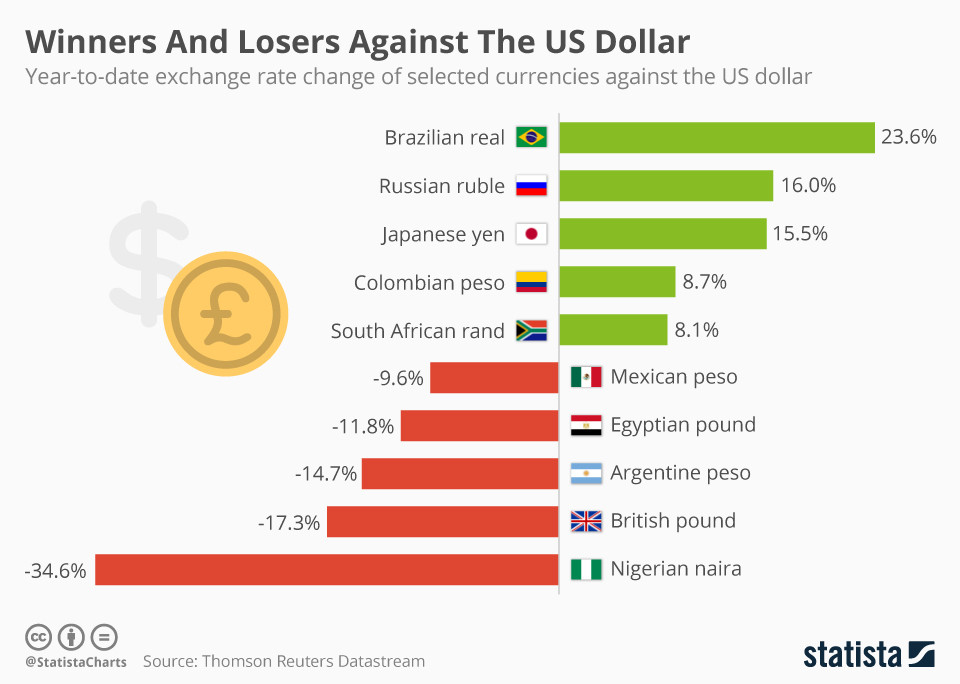
How can I start currency trading?
There are a few things you need to know before you get started in the world of currency trading. The first thing to understand is that there are two types of currencies: base and foreign. The base currency is the one that is being traded, while the foreign currencies are those that are being bought and sold. In order for you to trade in the forex market, you need to have a broker who will allow you to buy and sell currencies. You also need to be aware of the market hours, which vary depending on which part of the world you’re in. The global forex markets operate 24 hours a day, five days a week.
The second thing you’ll need to do before getting started in currency trading is choose your pairs wisely. There are many different pairs available for trade, but not all of them will be suitable for beginners. It’s important to focus on major pairs when starting out because they offer more liquidity and tighter spreads than minor pairs do. This means that it’s easier to execute trades at better prices with less slippage when dealing with major pairs than with minor ones.
Once you have chosen your pair (s), it’s time to get familiar with price charts. Charts provide traders with information about past price movements and can help predict future price action. Most charting platforms offer several different chart types, such as line charts, bar charts, or candlestick charts, so it’s important to find one that suits your needs.
Now that we’ve covered some basics, let’s take a look at what else beginner traders should keep in mind when getting started in this exciting market:
- Start small: When starting out, it’s important not to risk too much money on any single trade; begin by allocating just 2-3% of your total account balance per position.
- Use stop losses: A stop loss order ensures that if/when your trade goes against you, your losses will be limited.
- Stay disciplined: Like any other type of investment, successful currency trading requires patience and discipline.
- Monitor market conditions: Pay attention to news events and economic data releases that could impact prices.
A great variety of currencies are traded in the currency market.
The currency markets are a global marketplace where traders can buy and sell currencies. All major national currencies, gold, and even several foreign currencies can be traded on an exchange. Each currency is called an “asset”, and there are many types of assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities.
The US dollar; Japanese yen; British pounds; euros; Chinese yuan; Swiss francs; Australian dollars; and Canadian dollars are the most commonly used currencies.
Each currency has unique features that affect its price in the market.
US Dollars: The dollar is the most commonly traded currency in the world. It is used as a reserve currency by many governments around the world, and because of this demand, it usually has a higher value than other currencies.
Japanese Yen: The yen is often used as a funding or investment vehicle because Japan has low interest rates relative to other countries. This makes it attractive to investors looking for high returns on their investments.
British Pound Sterling (GBP): The pound sterling (GBP) was once considered one of the strongest global currencies, but its value has declined in recent years due to Brexit-related uncertainty.
Euros: The euro (EUR) was created in 1999 as part of efforts to create a more unified Europe. It now represents over 30% of all global transactions, making it one of the most popularly traded currencies in the world.
Chinese Yuan: In December 2015, China announced that they would begin allowing free convertibility between yuan and other foreign denominations, which made it easier for people to trade yuan outside China’s borders. This helped increase demand for yuan-denominated assets, driving up its price relative to other global currencies.
What are some common mistakes currency traders make?
As a currency trader, you are always looking to make profits by buying and selling currencies. However, there are some common mistakes that many traders make that can lead to losses instead of profits.
One common mistake is not doing your research before making trades. You need to have a good understanding of what is happening in the market so that you can make informed decisions about when and where to buy or sell currencies.
Another mistake is trading too often. This can lead to over-trading and poor decision-making, as well as increased stress levels. It’s important to only trade when you have a solid plan in place and are confident in your ability to execute it correctly.
In addition, many traders fall victim to greediness, wanting more money than they originally planned, which often leads them into bad trades with high risk potential. Trading should be seen as a business venture rather than a gamble; if you approach it with this mindset, then you’re more likely to succeed in the long run.
Conclusion
In this lesson, you learned about the currency markets and how they work. You also learned about the seven most important factors that affect a currency’s value. Finally, you read about a country’s economic zones and how they can impact a currency’s value.
The currency markets are an important part of the global economy. They allow people to buy and sell currencies from around the world, which helps to stabilize prices and create more efficient trade practices. The seven factors that affect a currency’s value are: interest rates, inflation rates, economic growth rates, trade balances, government debt levels, political stability and riskiness of a country, and foreign investment levels in that country.
Each of these factors can have a big impact on a currency’s value relative to other currencies. For example, if there is high inflation in one country but low inflation in another, investors may move their money out of the first country and into the second one because it is more stable economically speaking. This would cause the first country’s currency to lose value compared to other currencies on the market.

